By Helen Armstrong
“Companies need to figure out now how to survive in the future by selling less.” That was the message Professor Janet Godsell conveyed to female supply chain executives at Supply Chain Superwomen. The event, organised by Supply Chain Media to mark International Women’s Day, proved to be a unique opportunity to share supply chain challenges and visualise future scenarios in an open atmosphere.
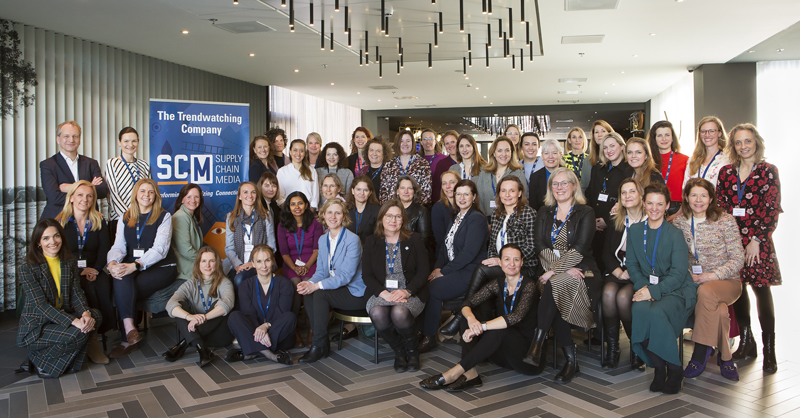
Female supply chain executives gathered from across Europe at a hotel at Schiphol Airport on 8 March to attend Supply Chain Superwomen. For many of the 45 participants, normally outnumbered by their male colleagues, the event proved to be an eye-opener as they suddenly realised how many women hold top positions in their field. Supply Chain Superwomen was an opportunity to support each other as role models and to encourage more women to run for top jobs.
Diversity leads to higher profitability
“We need to attract more women into supply chain,” said Martijn Lofvers, founder and chief trendwatcher of Supply Chain Media and chair of the event. “Not only do we have to enlarge the supply chain talent pool, we also know that diversity leads to higher profitability as it brings more insight, better decision-making and it drives innovation.”
According to a recent Gartner and Awesome report the percentage of women in the supply chain workforce in 2023 was 41%, compared with 35% in 2016. Just 34% of first line managers are female, falling further to 31% at senior management level and 26% at senior vice president level. “The percentage of women in supply chain is rising, but it’s not fast enough and requires more action by the talents themselves, their managers and HR managers. It is also imperative for the talents to have a supporting sponsor,’’ said Lofvers.
Building future scenarios
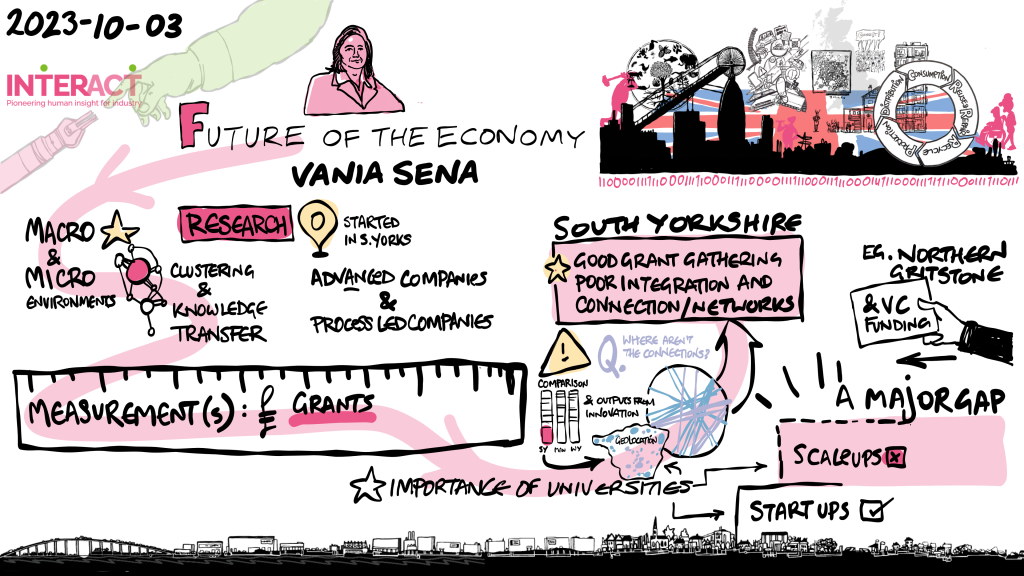
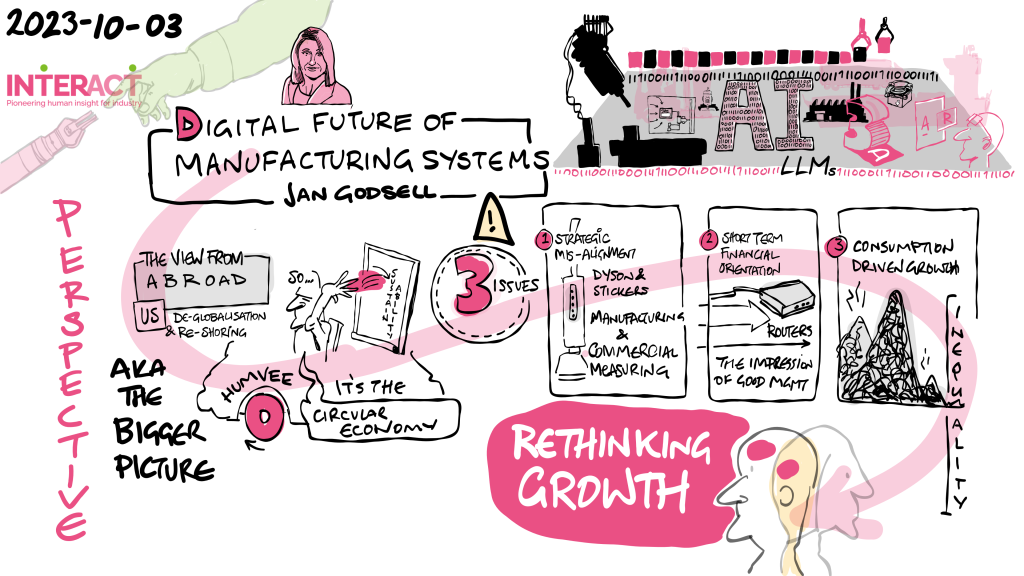
With the focus of the event on innovation, Professor Janet Godsell, dean of Loughborough Business School, UK, was invited to lead a workshop on building future scenarios to stimulate the delegates to think out of the box, to start a journey and to make a bolder first step.
“Women need to be brave in organizations to make disruption,” she said. “Since the industrial revolution we have pursued consumption-driven economic growth based not on what we need but on what we want. Now we recognize that this is destroying the planet, hampering social equity and widening the gap between rich and poor,’’ said Godsell.

Surviving with less sales
‘‘Today we are at a pivotal point and we need to make a fundamental change in the way we pursue growth in order to better balance the environmental, social and economic cost of growth. Looking to the future we have to consider the challenges, the trade-offs and the opportunities. Companies today have to work out how to survive in the future by selling less.”
With that in mind, the workshop based on backcasting, a visual approach to scenario-building by creating postcards, stimulated discussion, decision-making and most importantly drawings that depicted the future, in this case 2040. “Backcasting tries to shake people out of their current mind-set and to get them thinking differently about how a digitally-enabled supply chain can look,” explained Godsell.
Dragon’s Den
Earlier in the day three start-ups were invited to enter the Dragons’ Den and deliver their pitches: Lox Solution, which coordinates all carriers during the last-mile delivery, The Climate Choice, an intelligence platform that collects and audits data to enable scope 3 decarbonization, and Winddle, a supply chain collaborative platform to create ecosystems.
The delegates were invited to spend their money – poker chips in this case – on the start-up that had most potential to help them with their supply chain challenges. While all three were relevant, managing sustainability was the biggest issue for many. Consequently, the winner was Lara Obst of The Climate Choice.
This article was originally published by Supply Chain Movement.