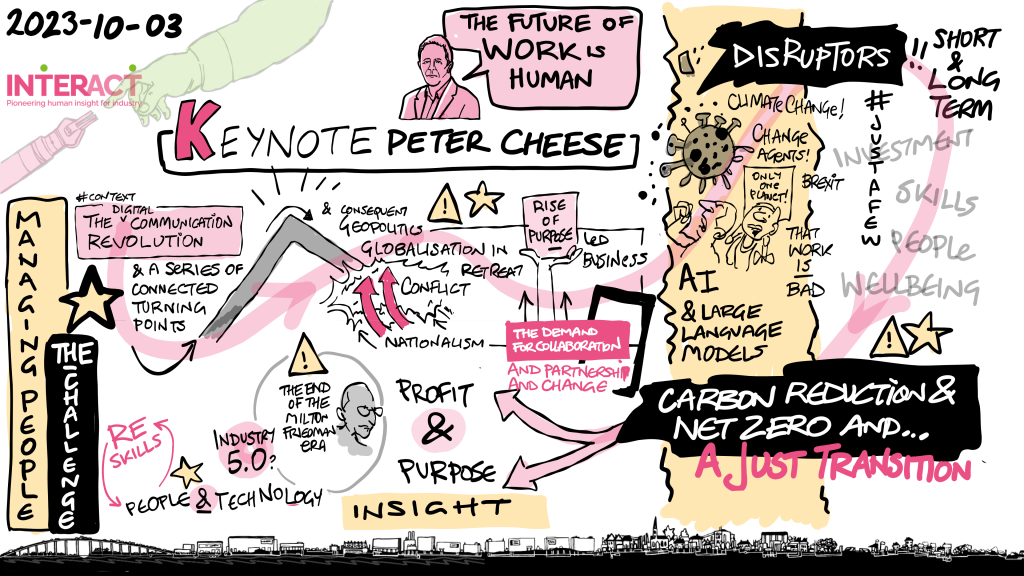
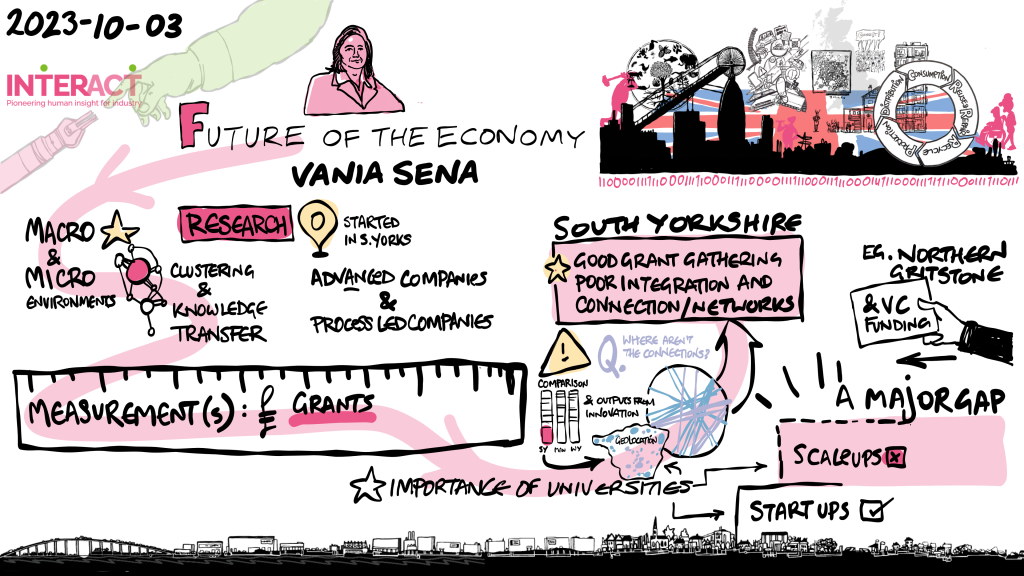
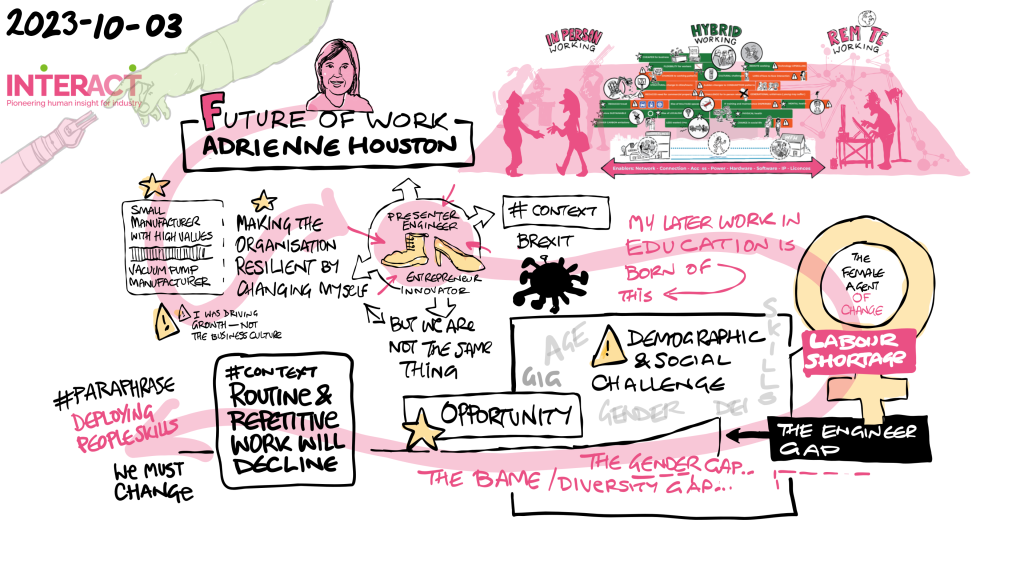
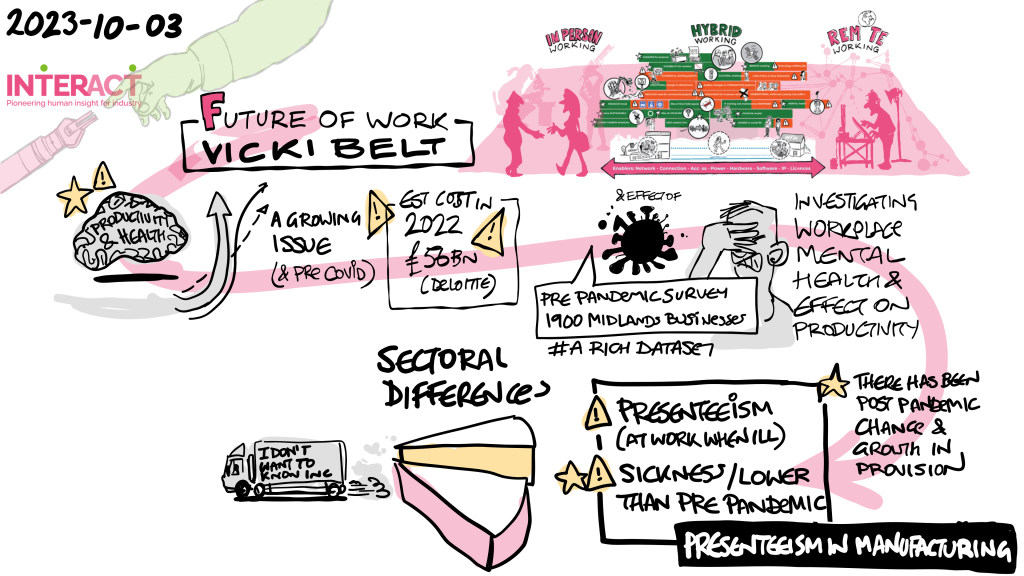
Overview
This research project examines the drivers, barriers, and performance outcomes of adopting industrial digital technologies (IDTs) in UK manufacturing firms. The findings outlined in the report and toolkit provide insights on the interventions that facilitate IDT adoption to enhance the performance of SME manufacturers exporting to international markets.
The project collected primary data from focus groups, interviews and a survey of 303 UK manufacturing SMEs currently exporting products. The outcomes from this primary research were used to develop an IDT adoption toolkit and decision-making model. This toolkit allows UK SME manufacturers to benchmark their level of IDT adoption against the industry standard, to identify which specific IDTs will have the greatest impact on improving their business performance across many indicators, and additionally can direct users to the digital solutions most relevant to their needs, thereby simplifying the process of IDT adoption.
Dr Hanh Pham, Dr Richard Hodgett and Prof Chee Yew Wong (University of Leeds). This work was supported by the UKRI Made Smarter Innovation Challenge and the Economic and Social Research Council via InterAct [Grant Reference ES/W007231/1].
For further discussions or to propose potential applications/collaborations, please contact Hanh Pham.
Please complete the captcha to download the file.
Download “Research report - Industrial digital technologies for UK SME exporting manufacturers”
IDT-adoption-research-report.pdf – Downloaded 14 times – 3.02 MB
Please complete the captcha to download the file.
Download “Toolkit - Industrial digital technologies for UK SME exporting manufacturers”
IDT-adoption-toolkit.pdf – Downloaded 11 times – 3.56 MB