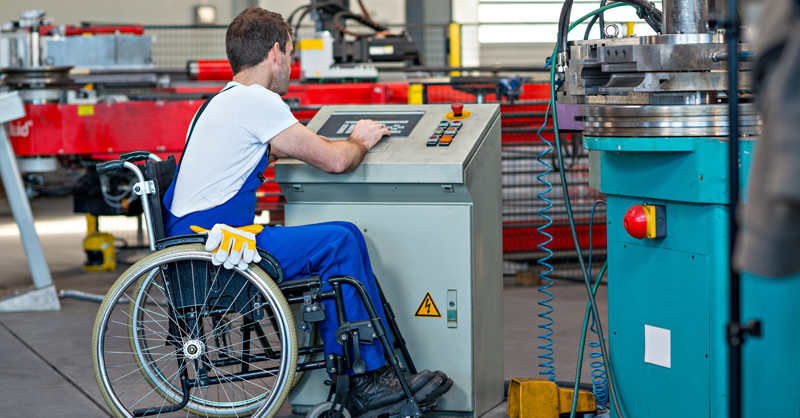
The manufacturing industry in the UK faces significant challenges in fostering diversity and inclusion, particularly regarding the employment of disabled individuals. While gender and ethnic diversity have been prioritised, disability inclusion remains largely overlooked, despite disabled people making up 23% of the UK’s working-age population. Persistent employment and pay gaps, alongside digital skill disparities, further hinder access to opportunities in manufacturing.
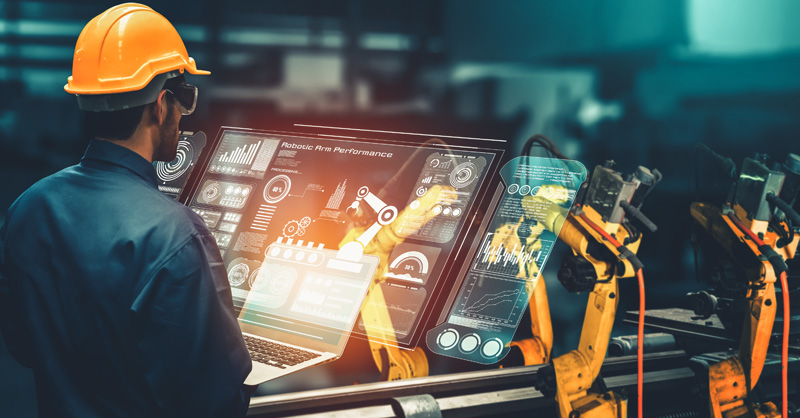
This project examined how digital technologies, inclusive management, and accessible business practices can bridge these gaps. Adopting a socio-technical approach, the project team envisions a future where technological advancements align with workplace inclusivity, supporting disabled employees through innovations such as AI-powered automation, VR training, and assistive robotics.
This report introduces a 2040 scenario, centring on Josie, a disabled manufacturing worker, to illustrate how technology and societal shifts can create an inclusive workforce. Insights from industry stakeholders validated the feasibility of these advancements but also highlighted barriers, including unequal access to digital tools and employer reluctance to accommodate disabled workers.
Key Visions for an Inclusive Future:
- Inclusive Society – Equal access to digital skills education and training from an early stage.
- Inclusive Technology – Enhanced accessibility to digital tools for individuals and SMEs.
- Inclusive Workplace – Overcoming physical and attitudinal barriers through flexible policies and leadership awareness.
Policy Recommendations:
- Inclusive Education & Training – Manufacturing skills programs must be tailored for disabled individuals.
- Collaboration Between OEMs & SMEs – Industry-wide partnerships to ensure accessible technology adoption.
- Supported Employment Initiatives – Proving the value of disabled workers in manufacturing through structured programs.
By aligning technological advancements with inclusive policies and workplace adaptations, the manufacturing industry can unlock the full potential of disabled workers, fostering innovation, productivity, and a more equitable workforce.
Please complete the captcha to download the file.
Download “Report - The Future of Inclusive Manufacturing through Digitalisation” InterAct-scenario-2040_inclusivity.pdf – Downloaded 6 times – 315.21 KB