Jennifer Castañeda-Navarrete
(IfM, University of Cambridge)
We are at a crossroads, with the opportunity either to progress towards a more equitable manufacturing landscape or to deepen existing gaps. The digitalisation of manufacturing provides a chance to transform the sector into a more inclusive and diverse one. However, if we do not take intentional and proactive steps, this digital transformation could instead reinforce prevailing norms and deepen gender inequalities.
In order to inspire and inform initiatives towards a more inclusive and diverse manufacturing sector, Cambridge Industrial Innovation Policy developed a policy brief to raise awareness about the challenges that women face when participating in manufacturing, while making the case for a gender-inclusive digitalisation. The policy brief was a key output of the InterAct-funded project Women in digital manufacturing and was conducted in collaboration with the Women in Manufacturing Initiative.
In this blog post, we will share some key takeaways from the policy brief.
What is the gender gap in UK manufacturing?
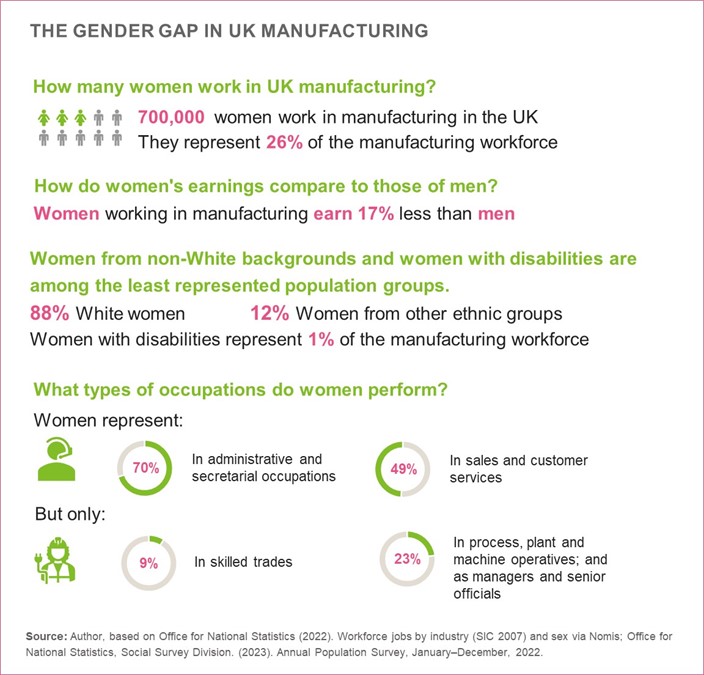
Gender norms and stereotypes segregate women and men into different occupations and economic activities. Although women represent almost half of the labour force in the UK, they account for just 26% of all workers in the manufacturing sector. Women working in the manufacturing sector earn 17% less than their male peers.
Women from non-White backgrounds and women with disabilities are among the least represented population groups in UK manufacturing. According to 2022 data, women from non-White backgrounds account for 15% of the workforce, representing just 3% of manufacturing employees. In the same year, women with disabilities, as defined in the Equality Act 2010, represented 9% of the people in employment; however, they made up for less than 1% of the manufacturing workforce.
Representation of women in UK manufacturing is markedly lower in skilled trade occupations (9%); process, plant and machine operatives (23%); and managers and senior officials (23%). In comparison, women’s representation is larger in administrative and secretarial occupations (70%), personal services (55%), and sales and customer service (49%).
Traditional gendered division of labour persists in manufacturing industries. Men mostly dominate the automotive industry, while the pharmaceuticals, textiles, and apparel industries have a more equal representation of both genders.
Unpaid childcare and household work disproportionately affect women’s participation in manufacturing. Women in the UK spend 1.7 more time a day in unpaid childcare than men and 1.4 more time in household work. This traditional gender-based division of unpaid work means that women face larger burdens to participate in paid work, particularly in positions with little flexibility or involving uncertain shifts and locations.
Because of this situation, women are more likely to work part-time than men. In 2022, 23% of the women working in manufacturing were working part-time, while only 5% of men were working part-time.
Challenges faced by women in the UK manufacturing sector
We invited stakeholders from the manufacturing sector to participate in an online survey to understand the challenges women face to participate in the sector. Survey participants perceive that the prevailing non-inclusive culture, which continues to favour men over women in manufacturing roles, is the primary hurdle to the participation of women in the industry. This is followed by barriers in promotion and leadership, a lack of awareness and visibility of job opportunities, a lack of skills and training support and work–life balance.
What are some of the challenges preventing equitable opportunities and rewarding careers for women in manufacturing?
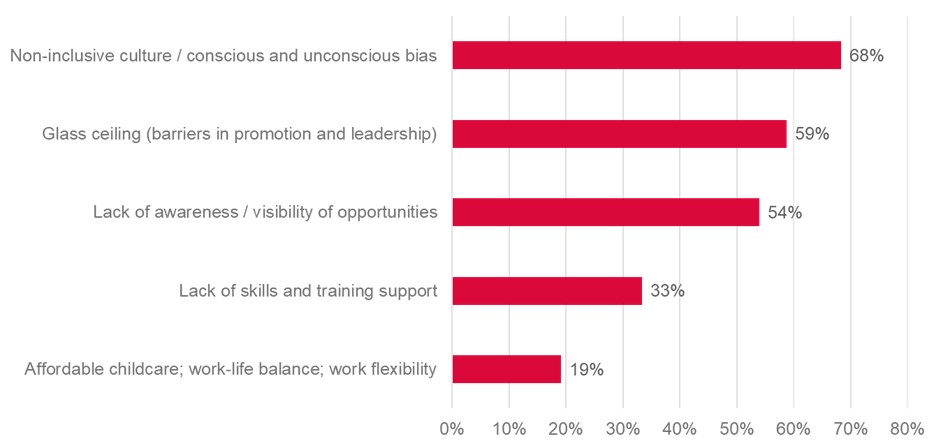
Note: Number or respondents = 63.The sum of the percentages exceeds 100% because respondents could select more than one choice.
Source: Women in Manufacturing survey.
The digital transformation and gender diversity in manufacturing
The digital transformation and other recent trends have had mixed effects on gender diversity in the manufacturing landscape. Over the past two decades, the UK manufacturing sector has significantly changed the distribution of job roles within its workforce. Despite labour shortages in roles such as process, plant and machine operatives and skilled trades, which men mostly hold, these positions have seen a notable decrease in their share of manufacturing employment.
Administrative and secretarial occupations, which are mostly held by women, have also seen a decline in employment rates, and this trend is likely to continue in the coming years. In comparison, there has been a substantial expansion in the shares of professionals and associate professional and technical positions.
Changes in manufacturing occupations, 2004 and 2022 (total)
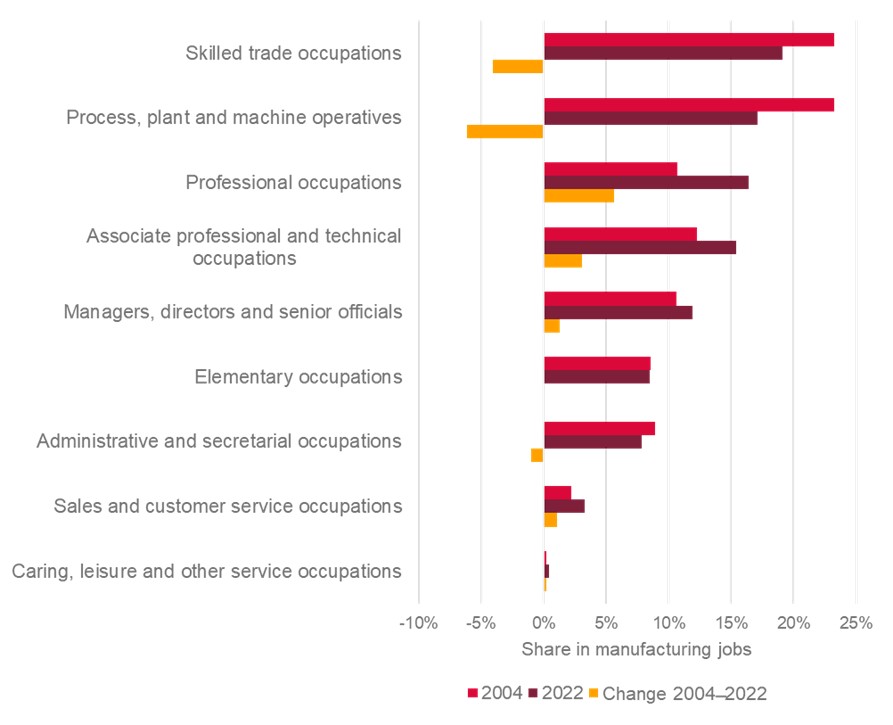
Source: Nomis. Annual Population Survey – Workplace analysis
Changes in the skills required by manufacturing businesses are creating opportunities for women to enter the industry. Skills such as data analysis, forward-thinking and innovation are becoming more relevant, and a growing number of women from different backgrounds have these skills. This positive trend is compounded by the interaction of the digital and the environmental sustainability transitions, which are making manufacturing more diverse.
From 2004 to 2022, there was an increase in gender diversity in several manufacturing jobs. These include professional roles, managers, directors and senior officials, associate professional and technical roles, and skilled trade occupations.
Changes in gender diversity IN manufacturing occupations, 2004 ̶ 2022
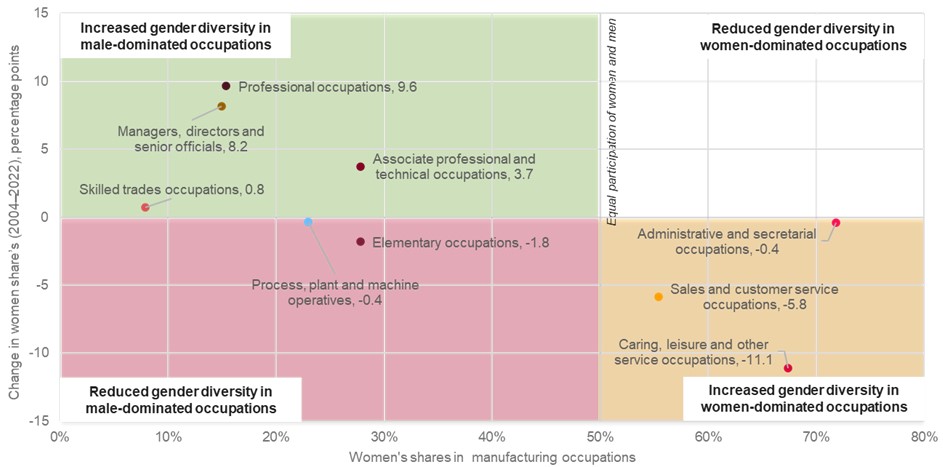
Source: Author, based on Nomis. Annual Population Survey – Workplace analysis. For detailed definitions of the nine occupational categories please refer to Appendix A of the policy brief..
The way forward: How can we improve gender diversity in UK manufacturing?
Drawing upon established practices to promote gender equality, 10 practical recommendations are provided in the policy brief for UK organisations to cultivate a more diverse and inclusive manufacturing sector.
Businesses, industry associations and research organisations could:
- Collect and analyse diversity data. According to the Make UK ED&I Survey 2021, 47% of manufacturers are not assessing the status of equality, diversity and inclusion.
- Promote an inclusive workplace culture through initiatives such as awareness-raising campaigns, diversity and inclusion training and networking opportunities.
- Address gender bias in recruitment and promotion by using inclusive language in job advertisements, promoting diverse interview panels and candidate pools, and promoting mentoring opportunities.
- Support work–life balance by providing flexible working arrangements, implementing return-to-work policies, promoting the uptake of paternity leave, and offering on- or near-site subsidised childcare, among other initiatives.
- Share and recognise examples of best practice by creating spaces for organisations to share their experiences and establishing awards to encourage outstanding practices.
Government organisations could:
- Follow a gender-transformative approach in government support programmes. This includes setting targets for reaching women-owned businesses through support programmes, including women’s business organisations in the design of dissemination campaigns, and conducting gender-sensitive evaluations.
- Support research on gender equality and gender-disaggregated data collection. We cannot address what we do not know. A critical gap exists in gender-, ethnic- and disability-disaggregated data, as well as in understanding gender differences in the adoption of digital technologies in manufacturing. Bridging this gap requires both allocating funding to expand survey samples and supporting new research.
- Incentivise gender equality in research and innovation teams by continuing efforts such as Innovate KTN’s guidelines for inclusive design and by including gender equality criteria in research and technology fund allocations.
- Adopt a lifelong learning approach in training and education programmes by creating opportunities for women to develop skills at different stages of their lives.
- Ensure an enabling environment for improving gender balance in caring responsibilities. This may involve cross-ministerial coordination and collaboration with industry associations to develop and enforce policies that support flexible working, paternity leave, returning to work, and child and adult social-care provision.
The policy brief provides examples of how various types of organisations are implementing initiatives in these areas. These include from a medium-sized business pioneering flexible working in manufacturing, to comprehensive equality and inclusion strategies in a multinational company, and gender-inclusive approaches in digital manufacturing support programmes.
Promoting gender equality not only upholds a fundamental human right but also serves as a catalyst for improved financial and environmental performance, making it imperative to prioritise the increased participation of women in the UK manufacturing sector. The potential economic benefits, as estimated by Make UK, underscore the vital role of gender diversity in closing skills gaps and driving economic growth, potentially adding £7 billion annually to the UK’s gross domestic product.
Finally, while the policy brief provides insights into the dynamics of gender diversity in UK manufacturing, shaped by digital transformation and other contemporary trends, there are still many unknowns that need to be addressed. For instance, we have little understanding of how digitalisation is changing manufacturing workplaces and the challenges women and men face in adapting to and benefiting from these transformations.
Despite increasing commitments to narrowing gender disparities, gender equality remains secondary in importance, particularly in industrial and technology domains. This oversight has resulted in underfunded research and analysis aimed at addressing gender gaps. To pave the way for a more inclusive, innovative, and equitable future in manufacturing, we must collectively tackle these outstanding issues.
Download the full policy brief:
Please complete the captcha to download the file.
Download “Policy brief - The case for a gender-transformative digitalisation”
Women-in-Manufacturing-policy-brief.pdf – Downloaded 3880 times – 3.97 MBThis work was supported by the UKRI Made Smarter Innovation Challenge and the Economic and Social Research Council via InterAct [Grant Reference ES/W007231/1].