Carolina Marin-Cadavid (University of Strathclyde)
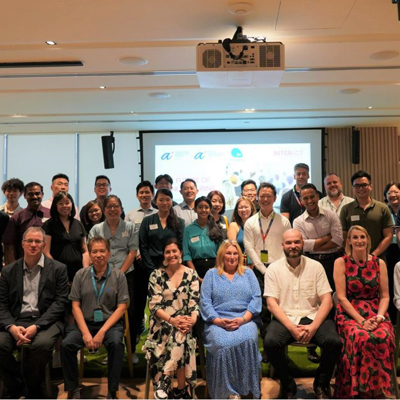
In June 2024, InterAct researchers visited Singapore as the first of several ‘Global Insight Missions’ aimed at uncovering new perspectives and knowledge from the global manufacturing ecosystem. This visit enabled the team to engage with the manufacturers, technology providers and support organisations that have driven Singapore’s advanced industrial development.
Manufacturing is not an isolated industry, tethered to any one country. To fully appreciate the scale of the challenges and opportunities for the global manufacturing ecosystem, it is essential we exchange knowledge with international partners and businesses. Our goal is to understand the competitive advantages of other countries, learn from them, and collaborate to share best practices and processes. This will help engaged stakeholders to address the challenges of digital transformation across three key areas: ecosystems, economies, and workplaces.
As part of our first global mission to Singapore, the InterAct team had the opportunity to visit a wide range of manufacturing and technology organisations such as:
- The Advanced Remanufacturing & Technology Centre (ARTC)
- The Singapore Institute for Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech)
- Augmentus
- Hyundai Motor Group Innovation Centre
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Halliburton
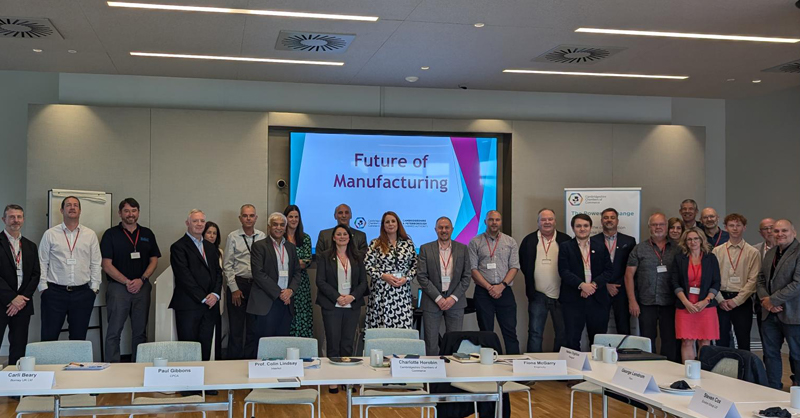
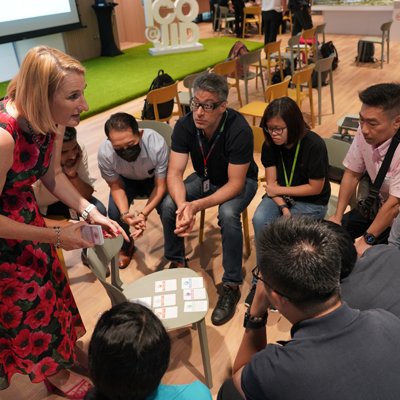
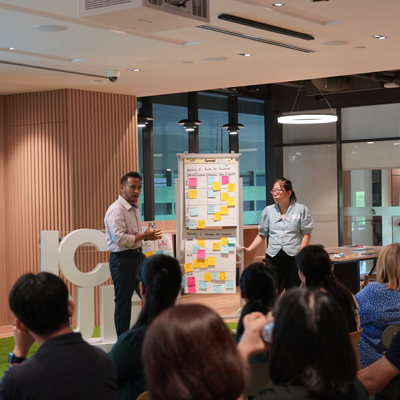
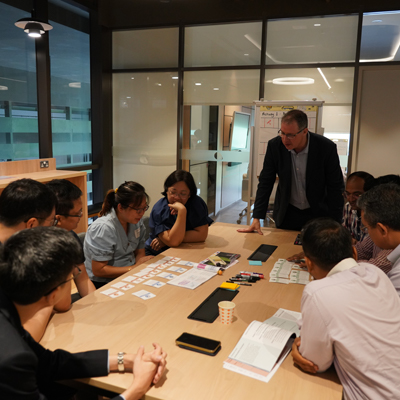
Additionally, InterAct hosted a collaborative workshop event in partnership with the ARTC, SIMTech, and the JTC Corporation sharing research generated from the Network’s Future of Work and Future of Digital Manufacturing Ecosystems projects, alongside insights on Singapore’s approach to digitalisation and sustainability.
Why visit Singapore?
This mission provided extensive opportunities to develop an enhanced understanding of the Singaporean approach to the process of digitalisation and manufacturing futures. Several key factors motivated the choice of Singapore as a destination for this initial visit:
- Singapore is recognised as an exemplar of successful economic growth. A significant aspect of this success is the role that the Singaporean government has played in shaping the nation’s economic system through an industrial strategy (WIPO, 2022).
- The strategy “AI for the Public Good, for Singapore and the World” was launched in 2023. This initiative aims to position Singapore as a “Smart Nation” to embrace digital transformation through driving global innovation (Smart Nation, 2024).
- Singapore is a hub for global manufacturers because they have access to talent, political stability, and geographical advantages for entering Southeast Asian Markets (Knight Frank, 2024).
- Singapore is also a start-up hub placed as second only after Silicon Valley (Heo, 2021).
- Public institutions assist people in upskilling and reskilling for emerging jobs. Singapore significantly outperformed many European countries in the training participation rate among unemployed residents aged 25 to 64 (Ministry of Manpower, 2023).
Building a better global manufacturing future, together
InterAct hosted an event supported by the Knowledge Transfer Office of the ARTC and SIMTech – two institutes belonging to the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR). This workshop was delivered with local stakeholders from both local and multinational manufacturing companies in Singapore.
Organisations participating in the event included 3M, Mitsubishi, Edwards, Kowa Skymech, and Halliburton. The practitioners and stakeholders shared their challenges, drivers, and ambitions for achieving a sustainable digital transformation in the future.
Participants had the opportunity to explore ideas and visions around the future of the manufacturing sector, with particular emphasis on what they believed like scenarios and key drivers of innovation would be, highlighting factors such as:
- Singapore’s government is encouraging workers to develop skills and upgrade their proficiencies.
- Singapore is a hub for businesses and provides the infrastructure to develop digital capabilities.
- They are accelerating the pace of automation and building new autonomous technology access.
- A recurrent theme was the aim for workers to be more efficient, dynamic, and sustainable.
- They highlighted that the key gaps to achieve these primary targets are generating workplace competency, encouraging people to work with technology, and the contrast of individual mindsets vs the national outlook.
Key insights on Singapore’s manufacturing future
- The Advanced Manufacturing Training Academy (AMTA) in Singapore is supporting companies in transforming their human capabilities through a sustainable upskilling programme: ‘Learn, Practise, and Implement’. This programme is anticipating the future of workforce roles and skills.
- Due to its lack of natural resources, Singapore’s competitive advantage is its people. They focus on education by upskilling and reskilling their workforce, supported by the government. By developing new training in partnership with local institutions, Singapore is enhancing their digital capabilities for the future.
- Government funding and support are key to encouraging companies to pursue digital transformation and engage their high-level managers in upskilling and reskilling programmes.
- Roles are evolving, and manufacturing companies need more entrepreneurial and innovative leaders on the shop floor to make real-time decisions.
- Cybersecurity and sustainability are prominent challenges for SMEs in the manufacturing industry. In the UK, there is a need for an integrated vision where the enhancement of human factors is aligned with sustainability.
- MNEs from the manufacturing industry are relocating to Vietnam, Malaysia, and Indonesia, where they benefit from more physical space and available human resources.
- Due to the labour gap in Singapore, headquarters located in this market are accelerating processes and driving digital transformation for MNEs.
- Robots are enhancing working conditions by promoting a cleaner and safer environment for workers.
- Singapore is ranked 2nd worldwide for robot adoption, while the UK ranks 28th.
- Employees are encouraged to generate ideas, which are implemented through internal and external funding, creating an ecosystem of actionable intelligence.
- The accumulation of skills is crucial for transferring knowledge to future generations and building human capability.
- Singapore has an ambitious decarbonisation plan, despite challenges such as limited territory; importing 90% of its food, 50% of its water, and facing 30% risk of land submergence. They have established a ‘Green Skills Committee’ and are implementing the ‘Green Economy Regulatory Initiative’.
- Singapore is prioritising “extended producer responsibility” to achieve a circular economy.
References
Heo, S. 2021. Singapore still first in tech innovation hub global ranking: KPMG survey. The Business Times, https://www.businesstimes.com.sg/startups-tech/technology/singapore-still- first-tech-innovation-hub-global-ranking-kpmg-survey
Knight Frank. (2024). Singapore Researc: Industrial & Logistics. https://content.knightfrank.com/research/529/documents/en/singapore-industrial-and-logistics-market-update-q1-2024-11134.pdf Accessed on July 2nd, 2024
Ministry of Manpower. 2023. Labour Force in Singapore. https://stats.mom.gov.sg/iMAS_PdfLibrary/mrsd_2023LabourForce.pdf
Smart Nation. (2024). AI for the Public Good, for Singapore and the World. https://www.smartnation.gov.sg/nais/
WIPO. 2022. Global Innovation Hotspots: Singapore’s innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem. Geneva: World Intellectual Property Organization.