In today’s globalised business world, there is a growing need for ethical supply chain practices. Manufacturing companies are facing complex challenges in modern production, and the importance of transparency and accountability has never been greater.
In this article, leading InterAct funded researchers from the Institute for Manufacturing (IfM) at the University of Cambridge explore the potential of the industrial metaverse to help elevate ethical standards across supply chains. Examining the intersection of technology and ethics, the IfM team offers valuable insights into how manufacturers can navigate regulatory environments, build consumer trust, and promote positive social change.
In a world of globalised supply chains, manufacturing firms often lack awareness and control of their external operations, which can result in unintentional non-compliance with regulations. While forced labour generates $236 billion in illegal profits annually (International Labour Organization), European companies will soon have to show compliance with environmental and human rights standards within their supply chains.
In response to mounting concerns, Europe is poised to implement stringent measures to hold corporations accountable for their supply chain practices. The forthcoming ‘Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive’ heralds a new era of corporate responsibility. Large companies must conduct comprehensive audits of their supply chains, identifying and rectifying instances of forced labour and environmental degradation. Compliance will hinge on demonstrating adherence of the supply chain ecosystem to human rights and environmental standards.
The regulatory landscape is not confined to Europe alone. The UK, through initiatives like the Modern Slavery Act of 2005, has committed to fostering transparency within supply chains to eradicate all forms of worker exploitation. Moreover, further legislative reforms are on the horizon, promising a paradigm shift in corporate accountability.
How high is the risk of being penalised for suppliers’ actions?
Currently, the lack of production transparency allows non-ethical manufacturers to cut corners, giving them a competitive cost advantage that appeals to consumers. Unfortunately, many of these consumers are unaware of the wider context and end up supporting production that causes serious harm to societies and the planet.
Manufacturers can’t wait for new regulations about environmental and human rights standards in the UK. They must lead the development of digital tools for their production environments that delve into the existing supply chain data. This will demonstrate that their products are made with minimal adverse impact.
To enable this, it is crucial to make the production processes more transparent. One possible way to achieve this transparency is by leveraging augmented reality technologies, which can interpret and explain the existing complex data along supply chain echelons and incentivise the creation of new data sources.
So, in light of these developments, how can manufacturers ensure compliance with the new regulations and help uphold human rights and environmental protection?
The industrial metaverse: the foundation for a more transparent supply chain?
Recent research conducted by IfM (supported by the UKRI Made Smarter Innovation Challenge and funded via the Economic and Social Science Research Council (ESRC)-led InterAct Network) offers an extensive overview of 1,680 international studies which reveal how extended reality technologies can support UK manufacturing by demonstrating production provenance in the Industrial Metaverse.
The Metaverse is a term used to describe the merging of the physical and digital worlds. It was first introduced by Neal Stephenson in his novel Snow Crash and later popularised by Mark Zuckerberg with Meta, a social network in extended reality.
The Industrial Metaverse comprises a series of ‘snapshots of realities’ around the data on sourcing, production, and delivery of components of a manufactured product, which can be explored in augmented reality. By exploring the upstream supply chain of components leading to the product, manufacturers can identify risks and take corrective action to comply with upcoming regulations.
Deploying industrial metaverse technology in practice requires:
- access to data sources;
- software (e.g. Unity Engine);
- augmented reality headsets (e.g. Microsoft Hololens, Meta).
Although 3D virtual productions might look complex and expensive, new AI techniques such as Gaussian splatting can significantly reduce the cost of reality reproduction: a ‘reality snapshot’ can now be created by anyone using a smartphone. This means, UK manufacturers can demand the video screening of the production environment from potential suppliers at the procurement stage. This is where lower-tier suppliers are incentivised to agree to increase transparency in exchange for eligibility to sell products and services. Decentralised databases can be used to store this information at the supply chain level. It is important to note that creating fake snapshots could lead to legal repercussions and regulatory requirements.
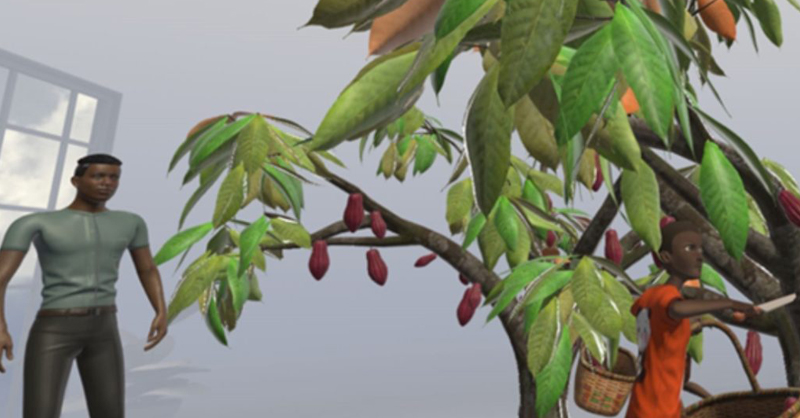
Case study: contrasting opaque and transparent chocolate supply chains
Agriculture is almost uniquely resistant to technological change because of the remoteness/lack of oversight/scale of sites, and it is an area desperately in need of innovation. Leading chocolate brands have long been criticised for neglecting ethical standards in cocoa procurement, and many of the brands can’t effectively enact change since the market behind wholesalers is not transparent. This situation creates a high risk potential for social injustice and modern slavery, i.e. when the wholesaler purchasing prices make cocoa sales below the point of profitability, and farmers are forced to take children out of school to work on the farm.
Industrial metaverse, established along such supply chains, can spur transparency and influence to change the status quo. As European consumers are the primary market for cocoa harvesting, they have the market power to improve conditions for farmers in West Africa. To end forced labour and enable children to access education, requires new tools that support the transparency of cocoa supply chains for consumers.
While labour and environmental abuses exist in many supply chains, shocking 60% of cocoa-growing households in Ghana’s upstream cocoa supply chain are estimated to use child labour. Ensuring manfuacturers and consumers have access to accurate information about these unethical practices is therefore an urgent issue. A famous example of good practice is the ‘Bean to bar’ Tracker, along with QR codes, barcodes, biological markers of specific farms and fermentation processing locations, all of which can link chocolate bars to their potential origin. By comparing the known land size of a farm and the claimed cocoa harvest from that land, we can identify if cocoa of unknown origin is blended into the batch. While such tools are currently being used internally for supply chain traceability, adding an Industrial Metaverse component can open up and showcase the evidence to consumers. Consumers will be able to witness vivid experiences demonstrating the potential impact of supporting the chosen brand. This can showcase the positive changes to society (e.g. freeing children labouring to get an education) or highlight negative practices (e.g. the realities of environmental damage or modern slavery). Such evidence can build a strong identification that by purchasing ethical brands, consumers will be supporting the continuity of ethical production practices and local communities’ upstream supply chains.
Transforming production practices in the industrial metaverse
The Industrial Metaverse will increasingly move from merely representing reality, to shaping it. By shifting demand to ethical products, manufacturers will be able to increase their production scale, reducing the cost per unit and creating a greater impetus towards sustainability.
Instead of waiting for new regulations about environmental and human rights standards to be implemented in the UK, manufacturers must lead the development of similar immersive experience prototypes to confirm the ethics of their production environments. Going beyond the food production case, electronics and automotive manufacturers can validate their production processes by establishing an industrial metaverse around their products and demanding ‘reality snapshot’ data from their supply chains. It will propagate the impact across supply chains towards reaching multiple firms worldwide and make production more transparent for consumers. Not only will that reduce risks of non-compliance with upcoming regulations, but it will also anchor consumer demand with positive societal changes along supply chains. By doing so, manufacturers can champion Sustainable Development Goal 12: “Responsible Consumption and Production”.
What practical steps should manufacturers take from this?
- Audit internal cost structures and visibility of operations along supply chains. Instead of aggregating costs at the wholesale level, manufacturers must enquire about the work conditions, energy sources, and potential carbon dioxide emissions through supply chain tiers.
- Collaborate with extended reality solution providers to prototype Industrial Metaverse around their products and reveal production ethics along supply chains.
- Analyse the integrated data and leverage alternative ways to reduce ethical risks. Communication throughout the industrial sector will help address industrial concerns about data privacy and confidentiality, leading to the industrial standard.
The IfM is currently working on developing a metaverse pilot for highly regulated sectors like aerospace, automotive, and food. These industries have very strict regulations that limit transparency. The goal is to enable a more transparent supply chain, which would contribute to the adherence of human rights and environmental protection. If you would like to collaborate with the team, contact Dr. Nikolai Kazantsev – nk622@cam.ac.uk or IfM Engage.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the UKRI Made Smarter Innovation Challenge and the Economic and Social Research Council via InterAct [Grant Reference ES/W007231/1]. We thank Prof Letizia Mortara, Dr Michael Rogerson and Alice Mumford for their feedback on this article.
This article draws from the InterAct report ‘Manufacturing in the Metaverse’
This article was originally published on The Manufacturer