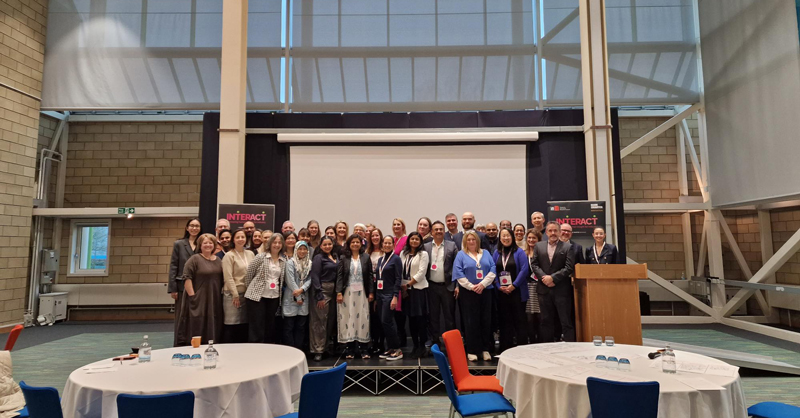
In February 2025, the InterAct Team visited Sri Lanka to contribute to the International Conference 2025 – Modern Challenges and Opportunities for the Apparel Industry in Colombo. The conference was organised by University of Monash and the JAAF ( Joint Apparel Association Forum). Sponsors included MAS Holdings, Star, Control Union, Omega Line, Sri Lanka Apparel, Postgraduate Institute of Management and InterAct.
Day One
The conference began with welcome addresses and an overview of sustainability and ESG initiatives from Australia, the UK, and South Asia. The keynote by Prof. Mohan Munasinghe emphasised the risks of climate change and nuclear war, calling for reduced emissions and conflicts. He noted China’s investment in clean technology versus the USA’s investment in war, and the shift in global GDP from G7 to BRICS countries. Prof. Munasinghe outlined three key lessons for sustainability: the importance of the triple bottom line, resource efficiency, and ethical values.
Control Union presented on various accreditation types, emphasising the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Discussions included digital product passports and the need for better data to track progress towards NetZero.
A panel discussion led by Associate Professor Glen Croy covered ESG impacts in the apparel industry. Participants highlighted the significance of community impact, alliances, and better measurement and data.
In the afternoon, a workshop led by Prof. Jillian MacBryde and Yufei Xue focused on shaping a sustainable future for the Sri Lankan apparel industry. Participants were invited to share their thoughts and ideas about ‘creating the future we want’ for Sri Lankan manufacturing, and offered insights including:
- Participants wanted to achieve sustainability through options such as zero landfill usage, renewable energy, ethical fashion, and circular economy models, focusing on reducing environmental impact and promoting responsible resource consumption.
- AI, smart manufacturing, distributed apparel systems, and advanced materials are recurrent themes, aiming to integrate cutting-edge technology in production, supply chain management, and product design.
- The importance of SMEs, investment in people, regulatory alignment, and capability building is essential, with a shift towards fair trade, transparency, and accountability across the supply chain.
- Participants emphasised a balance between revenue growth and ethical production, aiming for fair wages, worker well-being, and an inclusive ecosystem alongside financial success.
- Technology advancement is recognized as an vital driving force with a high positive impact on delivering the vision for the industry.
- Advanced technology offers avenues to improve productivity, quality, and efficiency in apparel manufacturing, enhancing sustainability practices, but requires significant investment in training, infrastructure, and research, while addressing job displacement and cybersecurity risks.
Day Two
The second day was a series of academic talks and discussions hosted by the Postgraduate Institute of Management (PIM). The day started with opening addressed by Professor Asanga Ranasinghe – Director, PIM and Professor Amrik Sohal, Chair of the Conference, Monash University. Keynote presentations were delivered by Associate Professor Glen Croy, Monash Business School, Monash University, Australia and Professor Jillian MacBryde, University of Strathclyde, Scotland.
Throughout the day, sessions focused on topics like: “People and Relationships”, “Circular Economy and Sustainability” and “Technology and Automation”. During these talks, it was highlighted that apparel exports from Sri Lanka are already between $4-6 billion in value per annum, with the sustainable apparel scope report suggesting that by 2032 the market could be worth as much as $24bn.
Day Three
On the third day of the mission, the InterAct team was able to visit a variety of local manufacturing sites, learning more about the operations of manufacturers in the region:
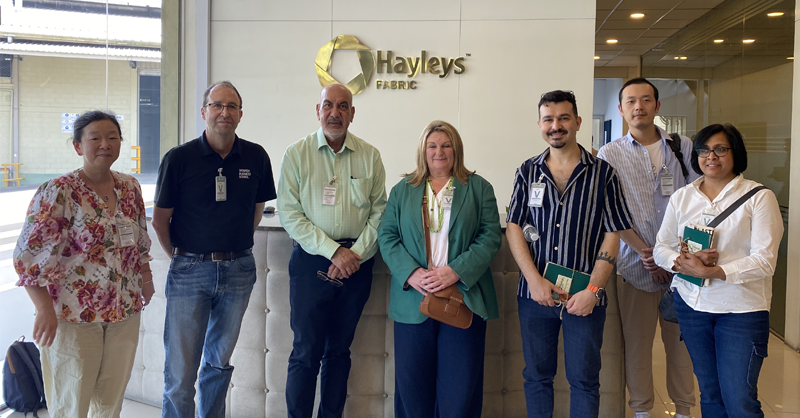
Site Visit 1: Hayleys
Hayleys, a fabric manufacturer deeply committed to ESG principles, emphasises their sustainability strategy “lifecode”. This approach focuses on going beyond compliance, committing to the basic rights of fresh air, water, and life, influenced by Buddhist culture.
Established in 1885, the South Asia Textiles factory the team visited is part of Hayleys, a multinational company with diverse sectors. The plant employs around 1,400 people out of 3,000 across the group. Working with big brands, Hayleys differentiates itself through innovation, product development, and sustainability.
At Hayley’s site we saw the centrality of ‘people’ practices to a manufacturing business, with strategic level consideration of employee wellbeing as a priority. With employees recruited locally, the business has fostered a strong sense of community and works on local initiatives including community health and biodiversity.
Site Visit 2: Eco Spindles
Eco Spindles, part of BPPL, focuses on PET waste collection and recycling, converting PET flakes to filament yarn using advanced technology.
They collaborate with brands like Decathlon, Tesco, and Nike, promoting sustainable business practice through various innovative product lines such as ECOS Green and Oceanic. Their marketing targets brand owners, garment manufacturers, fabric producers, and yarn manufacturers. Eco Spindles also engages in mechanical and chemical recycling of textiles, with significant investments in solar and biomass energy. The company has received numerous awards, including Forbes’ Best under £1 billion in 2021.
Site Visit 3: Star Innovation Centre
Star, established in 1978 and acquired by Komar, focuses on high-value apparel production with a workforce of 10,000 across 11 factories, producing 1.6 million garments a month. The Innovation Centre, located near the airport, is a carbon-neutral facility recognized as the Best Workplace in 2023.
Star focuses on key tenets of improving sustainability and implementing innovative technology, investing 2% of turnover in sustainability marketing and carbon credits. Despite the challenges of implementing new technology due to the unique characteristics of garment manufacturing, they have made significant investments in digital technology. Developments include: in-house design, 3D, and virtual reality, reducing sample making time and waste, while boosting overall productivity.
More details of our Sri Lanka mission and other Global visits will be available in our forthcoming InterAct Global report.